
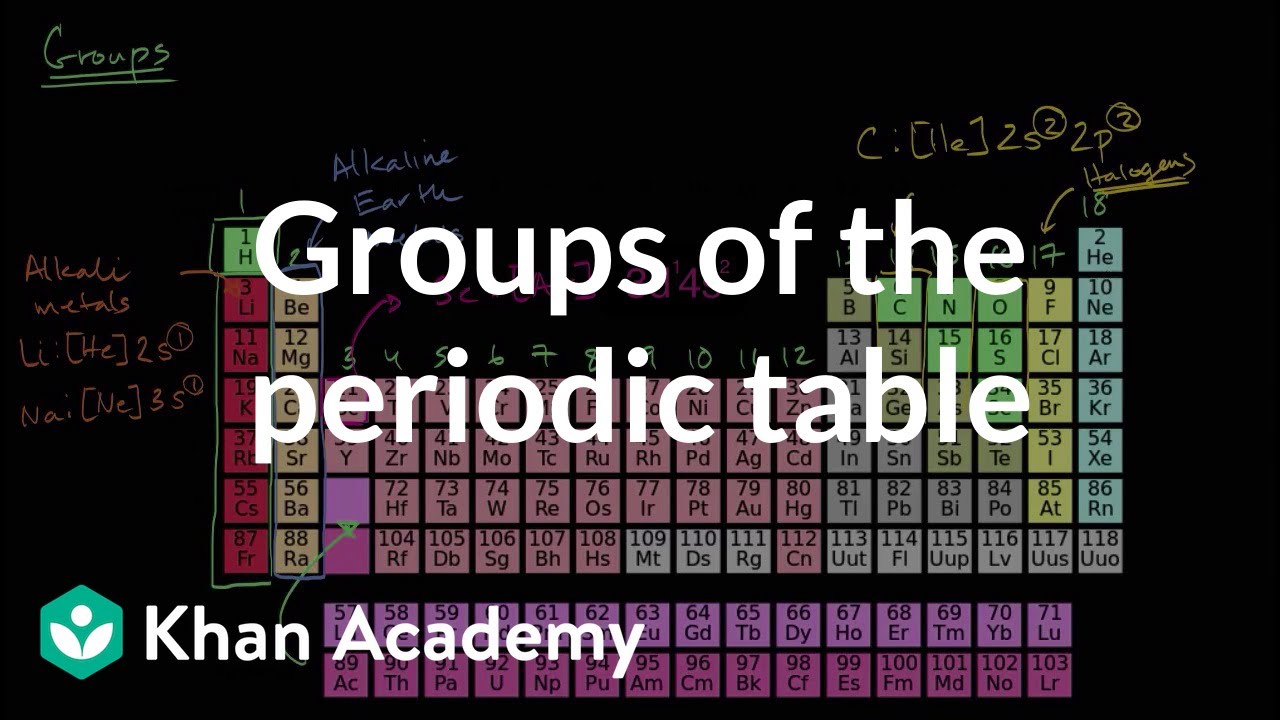
If you have eight protons, neutrons and electrons, you will have an oxygen (O) atom. When those pieces start combining in specific numbers, you can build atoms with recognizable traits. You know that a generic atom has some protons and neutrons in the nucleus and some electrons zipping around in orbitals. Trends are easy to find You will be responsible for working on the graphing periodic trends lab on your own time.Now we're getting to the heart and soul of the way the Universe works. A transition metal may lose one, two, or even three valence electrons depending on the element with which it reacts. Transition Metals The transition metals constitute Groups 3 through 12 and are sometimes called the d -block elements because of their position in the periodic table. Metals are recognized by its shiny appearance, but some nonmetal elements, plastics, and minerals are also shiny. Metals The majority of elements, including many main-group ones, are metals. With its one electron, hydrogen can react with many other elements, including oxygen. Because it consists of just one proton and one electron, hydrogen behaves unlike any other element. Main Group Properties Brainiac : The Alkali MetalsĪ class by itself Hydrogen is the most common element in the universe. alkali metals (Group 1) alkaline-earth metals (Group 2) halogens (Group 17) noble gases (Group 18) Main-group elements are in the s- and p- blocks of the periodic table. Main Group Elements Elements in groups 1, 2, and 13–18 are known as the main-group elements. The Periodic Law, continued Organization of the Periodic Table, continued Elements in the same period have the same number of occupied energy levels. A horizontal row on the periodic table is called a period. Elements in a group share chemical properties. Periodic Law A vertical column on the periodic table is called a group. īlocks of the Periodic Table Do not draw this! in Holt Chemistry! Elements with the same number of valence electrons tend to react in similar ways. Periodic Law Valence electrons are found in the outermost shell of an atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties. Elements in each column of the periodic table have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level (Valence Electrons). Periodic Law Mendeleev’s principle of chemical periodicity is known as the periodic law, which states that when the elements are arranged according to their atomic numbers, elements with similar properties appear at regular intervals. Moseley’s work led to both the modern definition of atomic number, and showed that atomic number, not atomic mass, is the basis for the organization of the periodic table īeyond Mendeleev When the elements were arranged by increasing atomic number, the discrepancies in Mendeleev’s table disappeared. Moseley studied the lines in the X-ray spectra of 38 different elements, he found that the wavelengths of the lines in the spectra decreased in a regular manner as atomic mass increased. īeyond Mendeleev About 40 years after Mendeleev published his periodic table, an English chemist named Henry Moseley found a different physical basis for the arrangement of elements.

Mendeleev predicted the properties of the missing elements. Mendeleev Mendeleev started a new row each time the properties of the elements repeated. Mendeleev wrote the symbol for each element, along with the physical and chemical properties and the relative atomic mass of the element, on a card. Mendeleev In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev used Newlands’s observation and other information to produce the first orderly arrangement, or periodic table, of all 63 elements known at the time. Newlands’ Law In 1865, John Newlands arranged the elements by atomic mass and noticed that physical properties repeated every eighth element. Despite the differences between elements, groups of elements share certain properties. Patterns in Element Properties Pure elements at room temperature and atmospheric pressure can be solids, liquids, or gases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
